Understanding FODMAP diet

FODMAP stands for fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols.
They are simple sugars that are poorly absorbed and rapidly fermented by the gut. when you consume foods that are high in FODMAPs, once they get to the intestines, they draw in water, increasing gas production.This type of dietary meal plan often is used to help with digestive symptoms from many different conditions, including, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), and other functional GI disorders.
List of Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Bloating
- Constipation/Diarrhea
- Distention
- Pain
- Gas
- Abdominal Pain
FODMAPs are in some foods naturally or as additives. They include fructose (in fruits and vegetables), fructans (like fructose, found in some vegetables and grains), lactose (dairy), Galatians (legumes), and polyols (artificial sweeteners).
These foods are not necessarily unhealthy products. Some of them contain fructans, inulin, and galactooligosaccharides (GOS), which are healthy prebiotics that helps stimulate the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. Many of them are otherwise good for you, but in certain people, eating or drinking them causes gastrointestinal symptoms.
Here are examples of FODMAP foods.
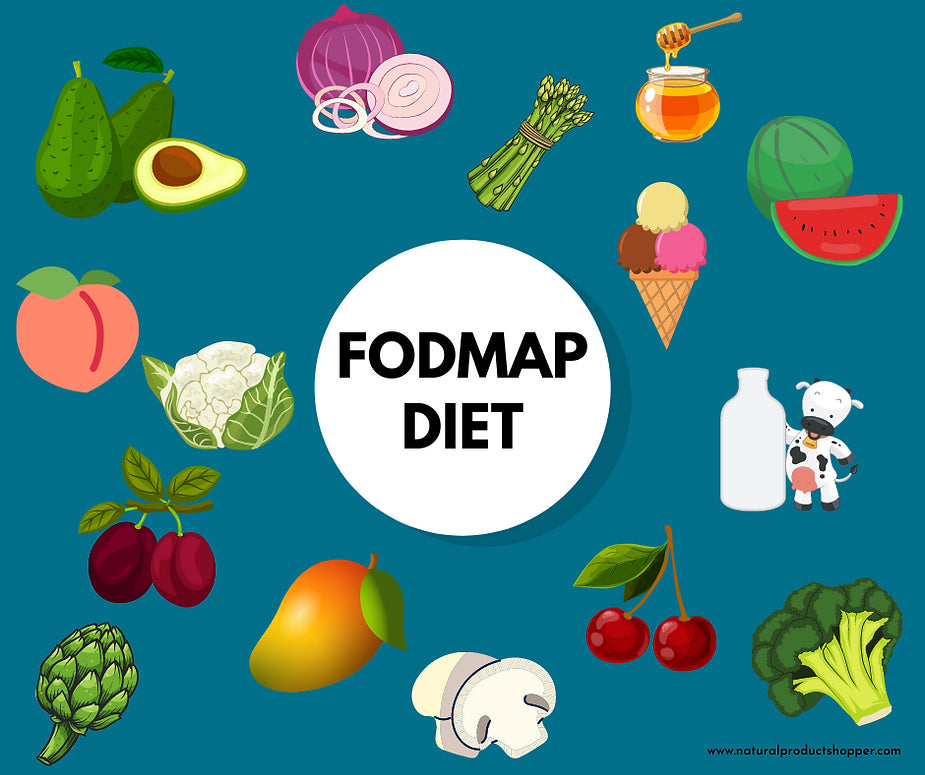
Experts have put together a “FODMAP elimination diet” that can be followed for a temporary time period. The diet is simple: avoid foods that are high in FODMAPs for a period of 2-12 weeks while focusing on foods that are low in FODMAPs. After that, individual foods can be introduced back into the diet, one at a time, to see whether that particular food or drink causes symptoms. If it does, you know you need to avoid that type of product. If no symptoms occur after consuming a particular food or drink for a week, it may be considered safe to continue to eat.It would not be good to avoid high FODMAP foods for longer than 12 weeks, as this can cause permanent damage or changes to your gut.
These are the 3 phases of eliminating FODMAP diet
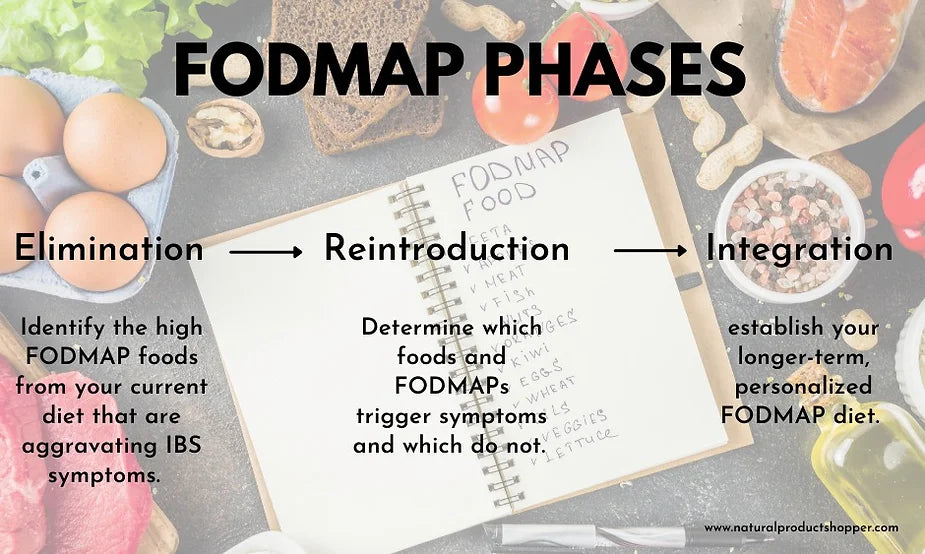
The first step is elimination. You have to switch to low FODMAP foods and avoid eating high FODMAP foods for 2-6 weeks. This has to be a strict diet for the process to work. After avoiding high FODMAP foods, the second step is reintroduction. In this phase it's handy to have a notebook and pen to list down all of your food intake of the day, Make a food diary. List the food intake of the day and the side effects of each meal to know what food to avoid eating,This approach will allow you to see which FODMAP groups you may have food intolerances to. You should take a break of a few days between the reintroduction of foods to avoid any crossover effects.Lasty, once you have established a list of what food your gut is reacted to, you should avoid eating these foods and have a lifelong lifestyle that's suits your gut health,
REMEMBER everyone’s food intolerances are different! Once your plan is in motion, this is the start of a stress-free life. Embrace your new lifestyle and live your life – your way!
